
amoeba Kids Britannica Kids Homework Help
Definition in Protistology In protistology, amoeba specifically pertains to the genus Amoeba (true amoeba) of the family Amoebidae, class Tubulinea. This genus is comprised of single-celled protists. They are free-living and feed on bacteria, other protists, or detritus.
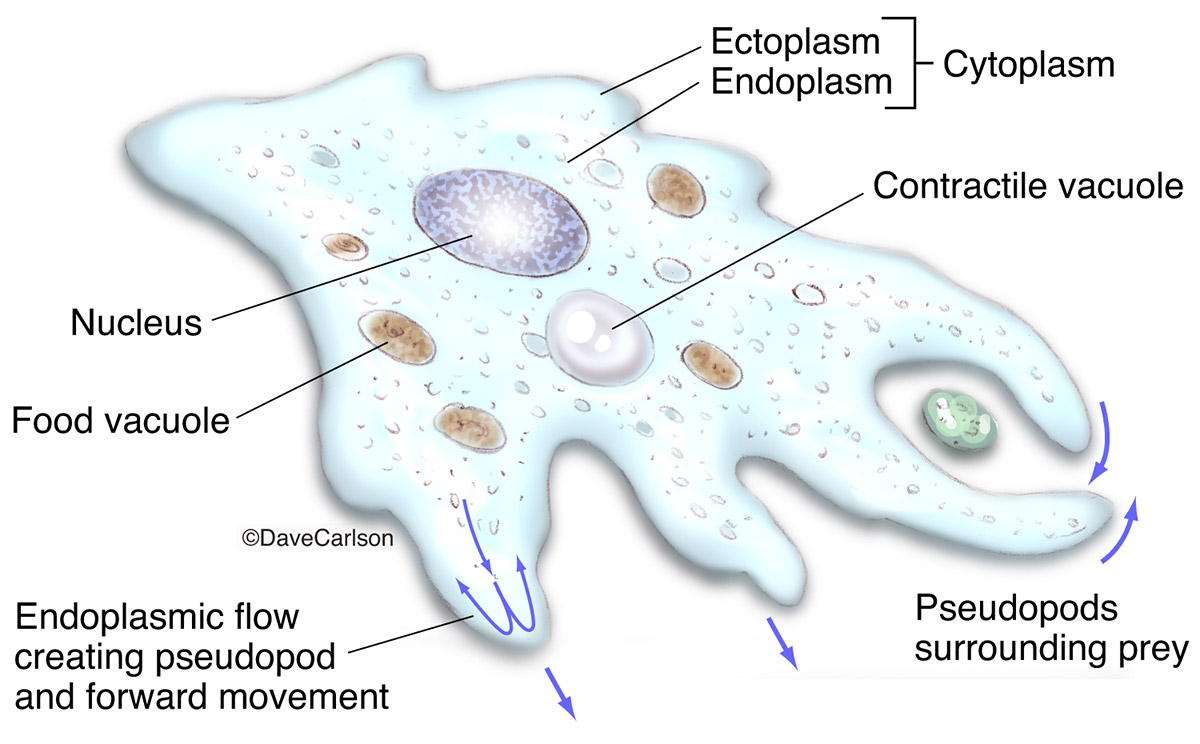
Amoeba Anatomy Carlson Stock Art
Pseudopods or Amoebas' false feet. A pseudopod is a temporary arm-like projection that is developed in the direction of movement. When the Amoeba stretches its pseudopods, the cytoskeletons (like the cells' skeleton system) inside the cell rearrange and extrude the cell membrane to change the cell shape. Once the tips of pseudopods adhere to the substrate, the cytoplasm of the cell flow to.

Structure of Amoeba Definition, Function, Classification, Nutrition and Parts of Amoeba
Amoeba Structure and Function Amoeba is a shapeless and colourless single-celled microorganism. It has a jelly-like structure, and it changes its shape. Its body is asymmetrical in shape. Its size is very small and can only be seen under the microscope. Its size ranges from 1 20 1 20 mm to 0.1 mm.
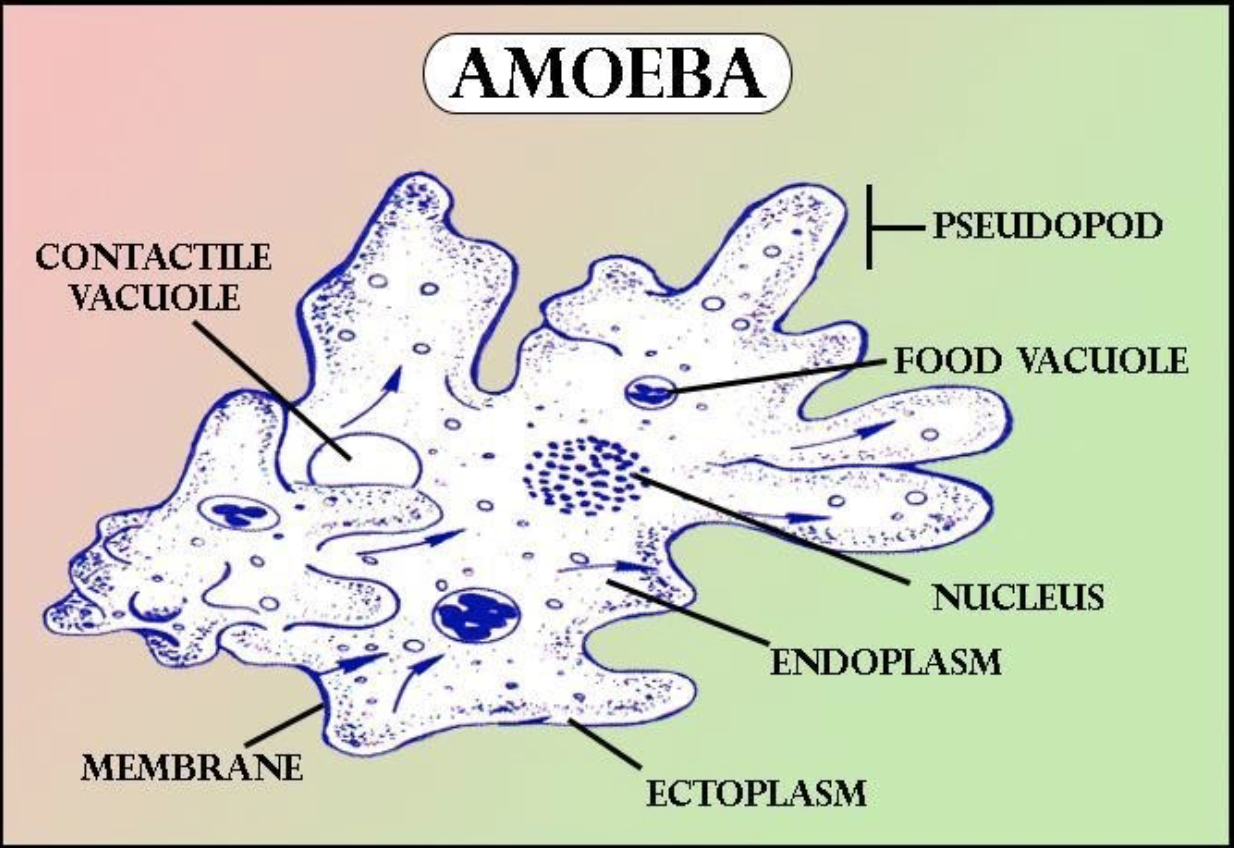
Who discovered Amoeba?
The Structure and Life Cycle of Amoeba (With Diagram) Article Shared by ADVERTISEMENTS: Read this article to learn about the Structure and Life Cycle of Amoeba ! Systematic Position Phylum: Protozoa Class: Rhizopodea ADVERTISEMENTS: Order: Amoebida Genus: Amoeba Species: proteus

PPT BIO1140 Lab 3 Cellular processes in Amoeba proteus PowerPoint Presentation ID2089001
1. Shape and size 2. Pseudopodia 3. Plasmalemma 4. Cytoplasm a. Ectoplasm b. Endoplasm 5. Endoplasmic organelles a. Nucleus b. Contractile vacuole c. Food vacuoles d. Water globules e. Other organelles Reference Classification of Amoeba proteus Phylum: Protozoa Subphylum: sacromastigophora Superclass: Sarcodina Class: Rhizopodea Subclass: Lobosia

Amoeba Structure Hand Drawn Image Stock Illustration Illustration of proteus, organelle 159548032
Shape, movement and nutrition The forms of pseudopodia, from left: polypodial and lobose; monopodial and lobose; filose; conical; reticulose; tapering actinopods; non-tapering actinopods Amoeba do not have cell walls, which allows for free movement.

Imagen de Proteus de la ameba con núcleo, vacuola contráctil, organelos y títulos Fotografía de
Structurally, amoebas closely resemble the cells of higher organisms. "They are like our cells, and in fact, when they are moving they look very much like our white blood cells," Maciver said.
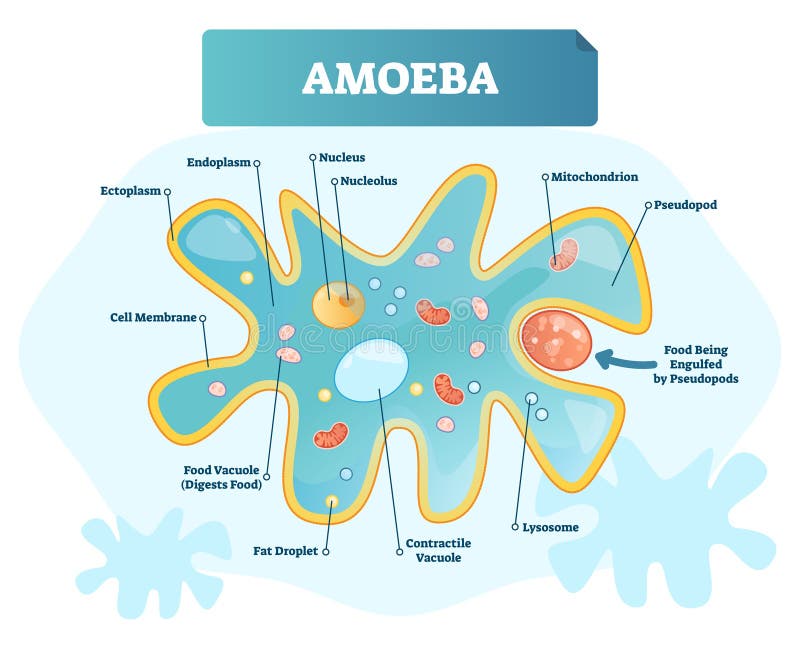
Büyükanne ve büyükbaba ziyaret girdap çalışma why do amoebas form pseudopods only when they need
amoeba, any of the microscopic unicellular protozoans of the rhizopodan order Amoebida.The well-known type species, Amoeba proteus, is found on decaying bottom vegetation of freshwater streams and ponds. There are numerous parasitic amoebas. Of six species found in the human alimentary tract, Entamoeba histolytica causes amebic dysentery. Two related free-living genera of increasing biomedical.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ameoba_feeding-56e30ae75f9b5854a9f8c0df.jpg)
Amoeba Anatomy, Digestion, and Reproduction
This movement strategy produces forward movement via the following three steps: "ballooning" the plasma membrane forward. This distinct rearrangement is known as a pseudopodium or "false foot", which is very similar in nature to that of the lamellipodium generated in higher vertebrates;
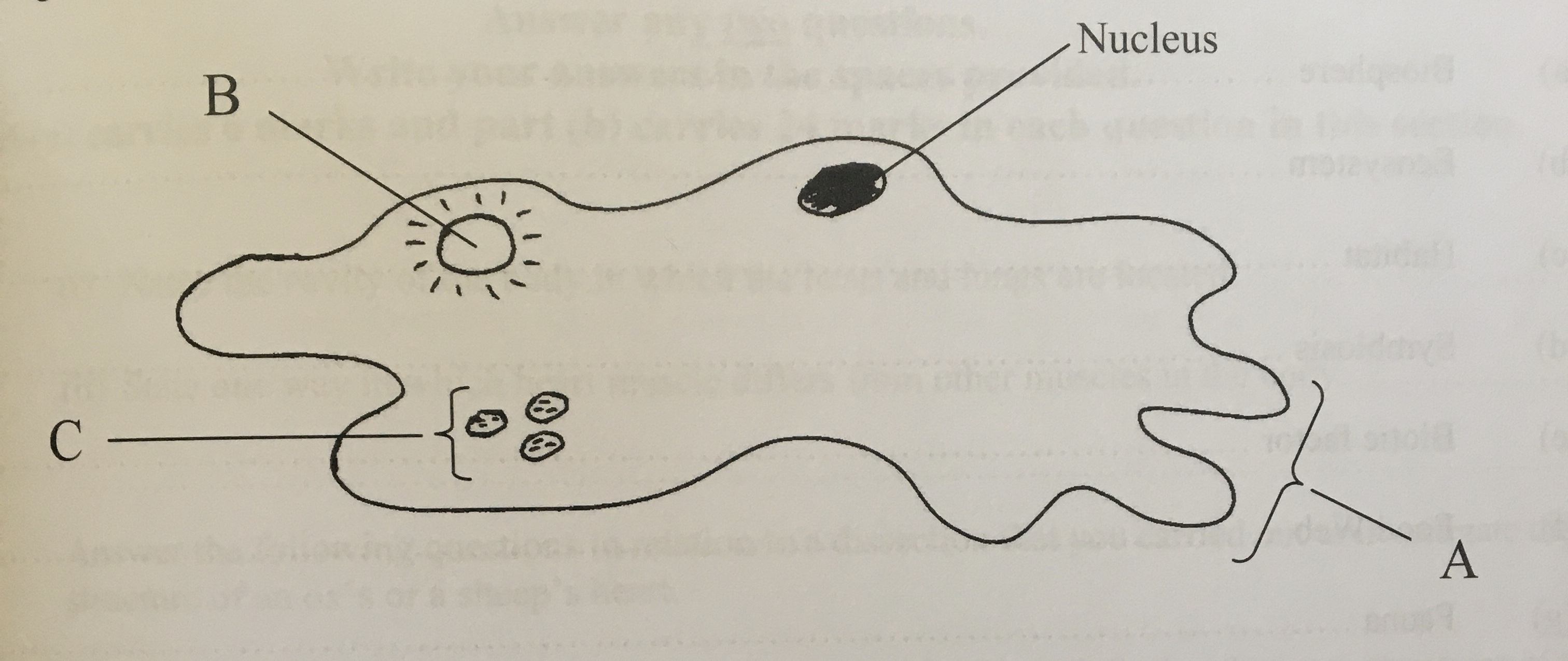
Amoeba Biology Quiz Quizizz
An amoeba is an aquatic, single-celled protist characterized by a gelatinous body, amorphous shape, and amoeboid movement. Amoebas can form temporary extensions of their cytoplasm known as pseudopodia or "false feet" which can be used for locomotion or capturing food. Food acquisition is amoebas occurs by a type of endocytosis called phagocytosis.

Amoeba Cell Characteristics, Structure, Movement, Nutrition, Reproduction, Disease, Habitat.
1. Cell membrane: Also called plasmalemma, it is a thin-layered membrane composed of protein and lipid molecules that restricts the entry and exit of substances in and out of the cell. 2. Cytoplasm: A mass of a jelly-like substance that holds all the other organelles. It consists of two parts:
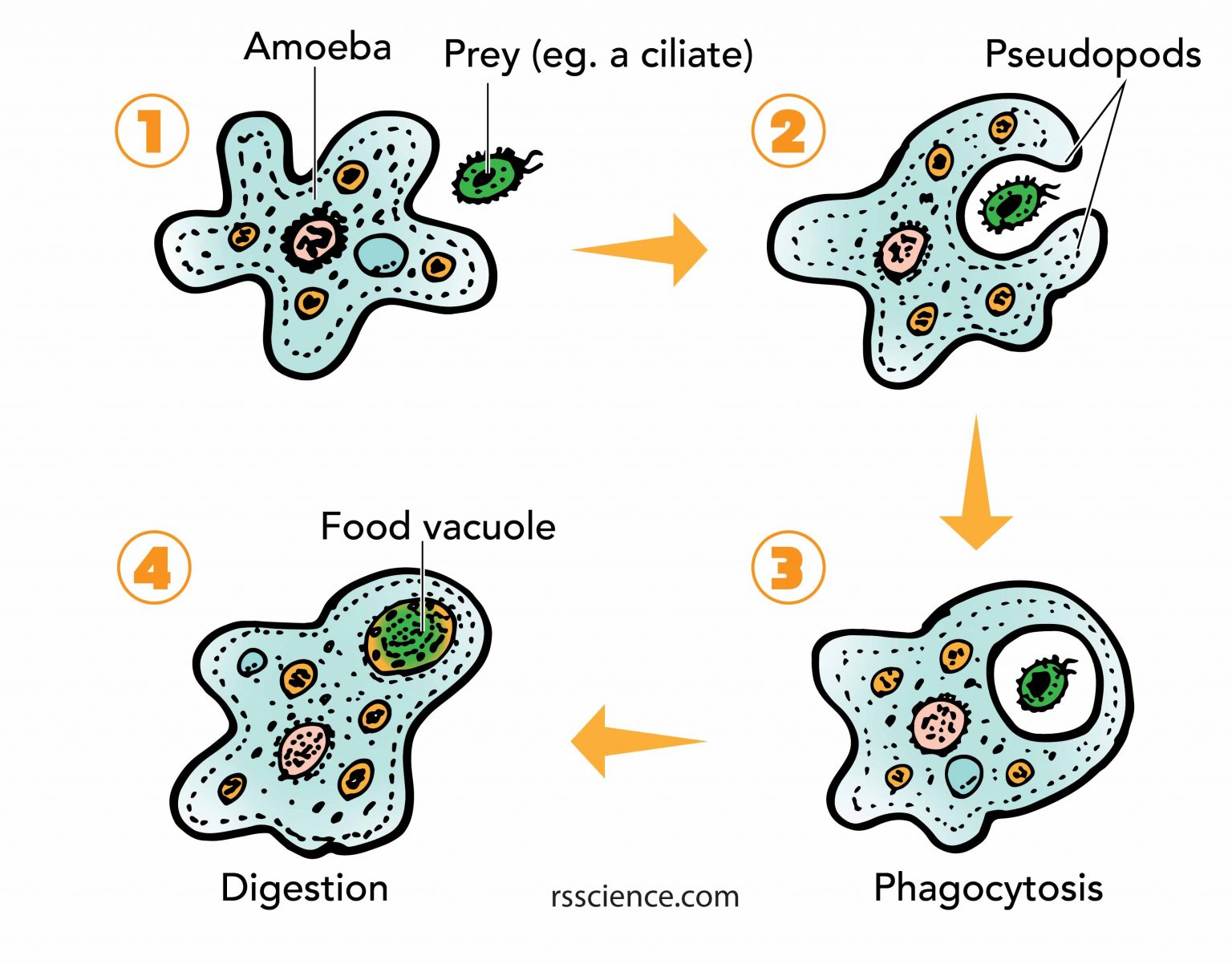
Facts about Amoeba, structure, behavior and reproduction Rs' Science
Amoebae are essential components of aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems and play a vital role in the dynamics of microbial communities, nutrient cycling, and energy flow (7, 8).They are also a potential threat to human health, as some of them are pathogenic or even lethal to humans (7, 9, 10).There are several excellent reviews on amoebae and their bacterial symbionts (11,- 15).

What is Amoeba? Definition, Structure, Classification, Nutrition
The structure of amoeba consists of an ectoplasm and endoplasm. Various organelles like the nucleus, chromatin granules, and food vacuoles are present in amoeba's structure. Culture Preparation of Amoeba Cell To grow and study amoeba cells in a lab setting, adequate culture preparation is essential.
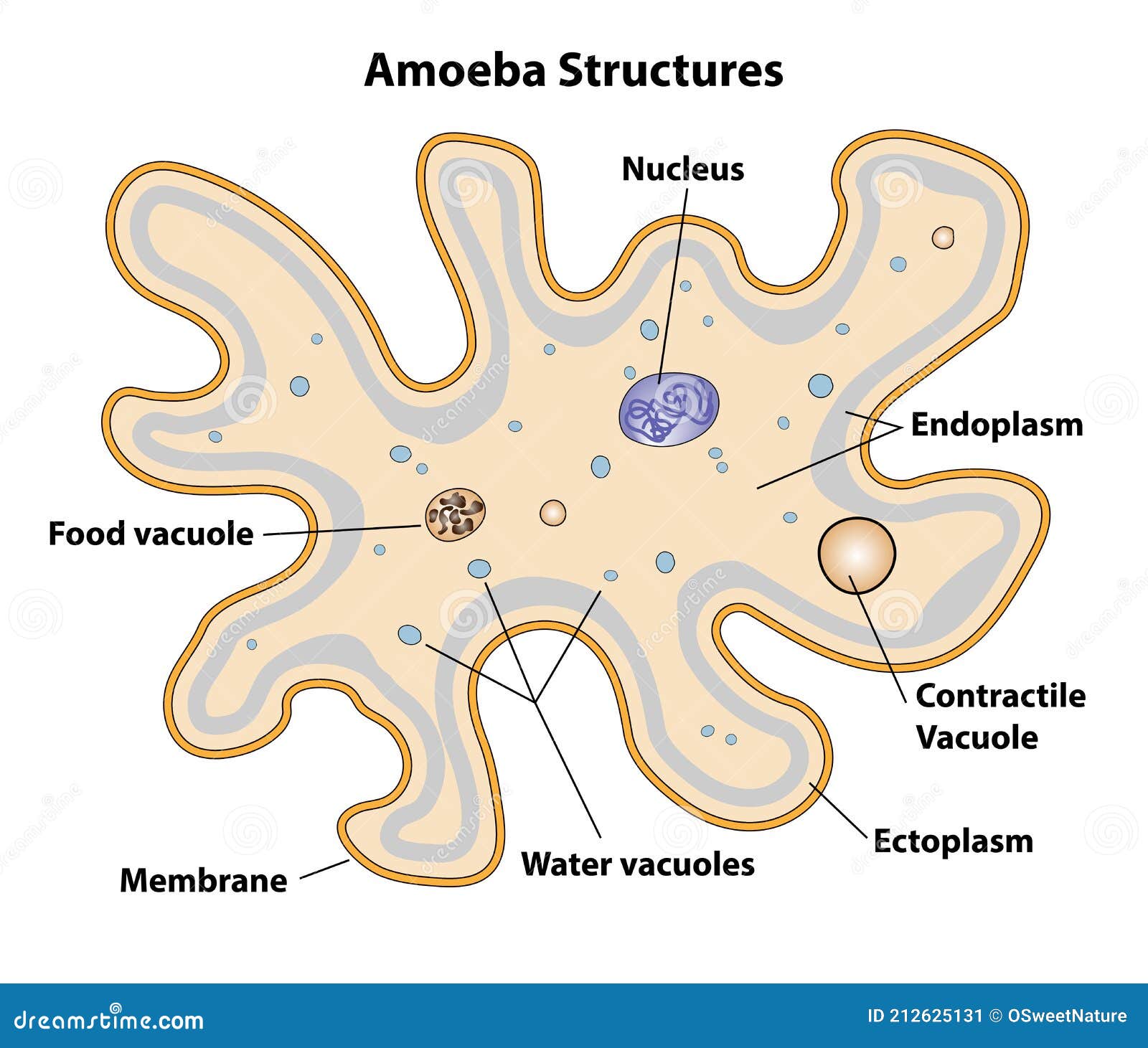
Amoeba
Handouts created by the Amoeba Sisters that correspond to Amoeba Sisters videos. The handouts are application oriented and supplemental to the more important thing like creating in the classroom and hands on labs.. Video includes all concepts from our old DNA Structure & Function video (which did not have a handout). Entire heredity playlist.
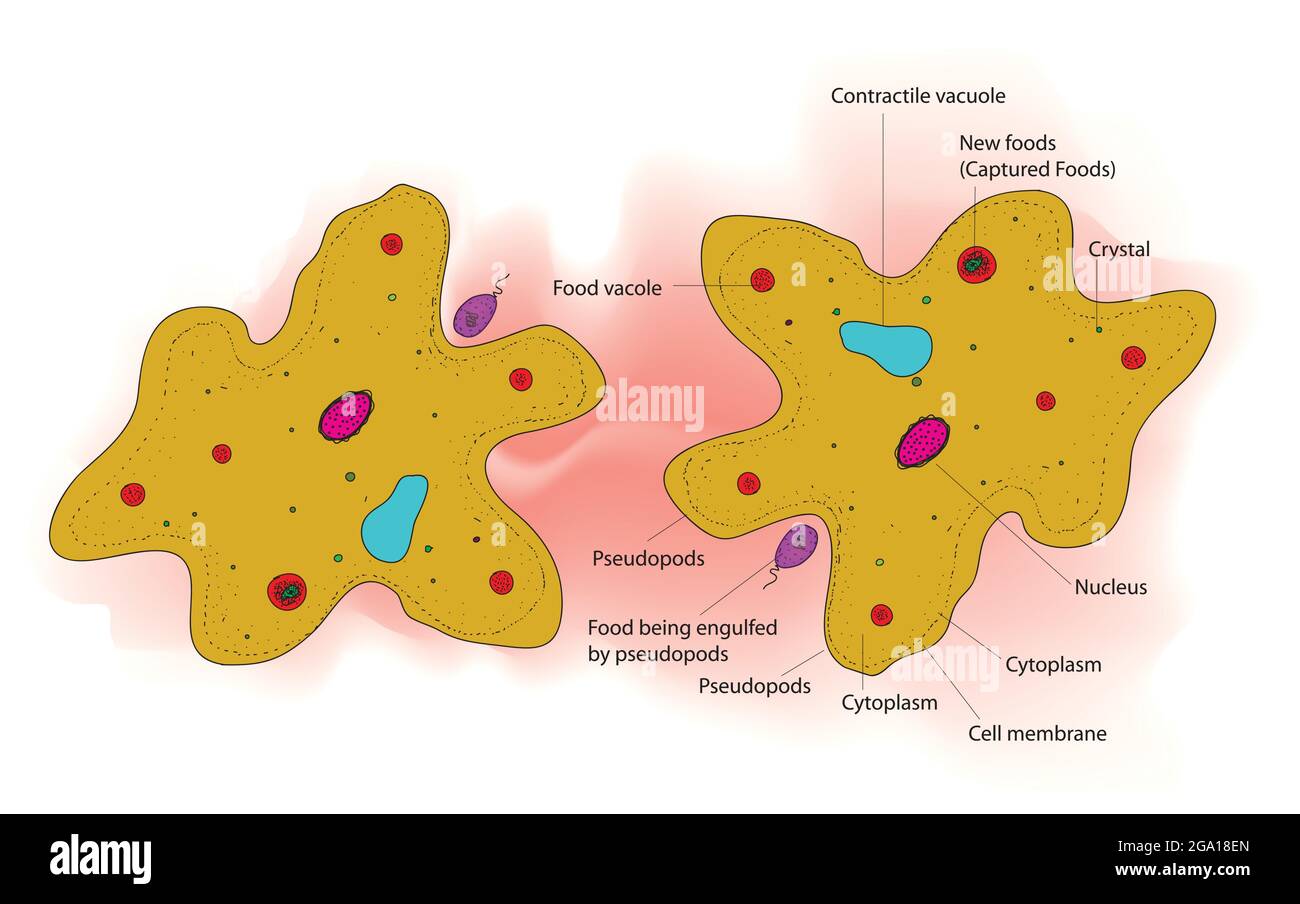
Structure of amoeba hires stock photography and images Alamy
Structure of amoeba primarily encompasses 3 parts - the cytoplasm, plasma membrane and the nucleus. The cytoplasm can be differentiated into 2 layers - the outer ectoplasm and the inner endoplasm The plasma membrane is a very thin, double-layered membrane composed of protein and lipid molecules.

Amoeba Biology diagrams, Biology notes, Science biology
Abstract. Amoeba proteus contains a central elongated fluid portion (plasmasol), a rigid layer surrounding this (plasmagel), a thin elastic surface layer (plasmalemma), and a hyaline layer between the plasmagel and the plasmalemma which is fluid at the tip of active pseudopods and in certain other regions. The plasmasol is an emulsion.